New Article in Steroids
Maria Misiak, Wiktor Koźmiński, Jacek Wójcik, Rafał R. Siciński, Jerzy Wicha

The application of 3D NMR experiments and DFT calculations enabled the structure investigation of C-17 epimer of 3-(25-hydroxycholest-5-enyl) acetate is presented. The H-17 and H-20 protons features the same values of 1H chemical shift, what causes that the structure elucidation require additional resolution enabled by 3D NMR experiments. The NMR experiments and theoretical calculations allowed for: the resonance assignment (3D COSY-HMBC and 3D TOCSY-HSQC techniques), the prediction of spatial structure (3D NOESY-HSQC and 3D ROESY-HSQC experiments), and the precise measurement of heteronuclear coupling constants (3D HSQC-TOCSY spectra with E.COSY-type multiplets).
New Article in Molecules
João M. C. Teixeira, Héctor Fuentes, Stasė Bielskutė, Margarida Gairi, Szymon Żerko, Wiktor Koźmiński, Miquel Pons
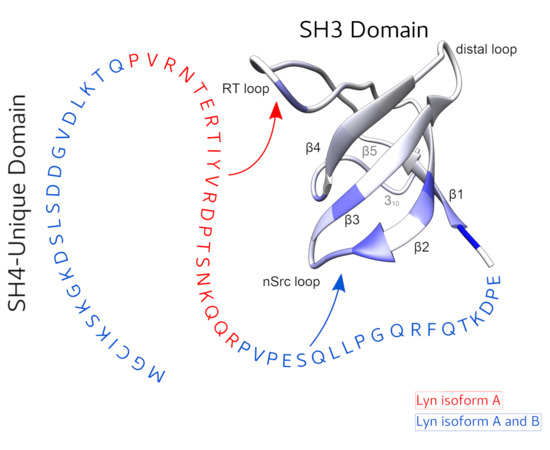
The function of the intrinsically disordered Unique domain of the Src family of tyrosine kinases (SFK), where the largest differences between family members are concentrated, remains poorly understood. Recent studies in c-Src have demonstrated that the Unique region forms transient interactions, described as an intramolecular fuzzy complex, with the SH3 domain and suggested that similar complexes could be formed by other SFKs. Src and Lyn are members of a distinct subfamily of SFKs. Lyn is a key player in the immunologic response and exists in two isoforms originating from alternative splicing in the Unique domain. We have used NMR to compare the intramolecular interactions in the two isoforms and found that the alternatively spliced segment interacts specifically with the so-called RT-loop in the SH3 domain and that this interaction is abolished when a polyproline ligand binds to the SH3 domain. These results support the generality of the fuzzy complex formation in distinct subfamilies of SFKs and its physiological role, as the naturally occurring alternative splicing modulates the interactions in this complex.
New Article in Journal of Physical Chemistry A
Sergey Molchanov, Tomasz Rowicki, Adam Gryff-Keller, Wiktor Koźmiński

1H NMR and 13C NMR chemical shifts as well as conformation dependent vicinal 1H–1H spin–spin coupling constants for cinchonidine in a dilute C6D12 solution have been measured. These data have been interpreted in detail exploiting the results of the extensive quantum chemistry calculations of molecular geometry and NMR parameters of the molecule, performed using the density functional theory (DFT) B3LYP/6-311++G(2d,p) polarizable continuum model (PCM) level of theory. The experimental values of NMR parameters for cinchonidine have been reproduced very well in terms of parameters calculated for key conformers of this molecule. Simultaneously, the analysis has provided us with a lot of information on conformational equilibrium of cinchonidine in the investigated solution. These findings remain in general agreement with the conclusions of other works, based on NOESY spectra or other physicochemical data. Thus, a careful quantitative interpretation of easily measurable NMR chemical shifts can be an independent and valuable source of structural information even in such complex cases as cinchonidine in solution.
|
New Article in RSC Advances
Anna Zawadzka-Kazimierczuk, Mate Somlyay, Hanspeter Kaehlig, George Iakobson, Petr Beierd, Robert Konrat
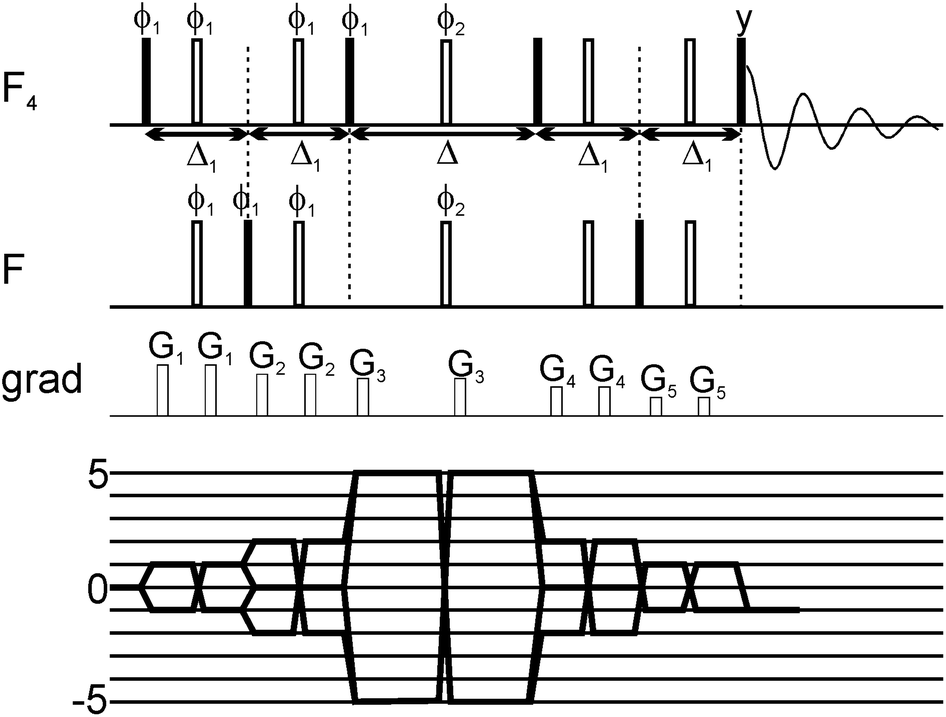
A new 19F NMR method is presented which can be used to detect weak protein binding of small molecules with up to mM affinity. The method capitalizes on the synthetic availability of unique SF5 containing compounds and the generation of five-quantum coherences (5QC). Given the high sensitivity of 5QC relaxation to exchange events (i.e. reversible protein binding) fragments which bind to the target with weak affinity can be identified. The utility of the method in early stage drug discovery programs is demonstrated with applications to two model proteins, the neurotoxic NGAL and the prominent tumor target β-catenin.
New Article in Journal of Biological Inorganic Chemistry
Chris A. E. M. Spronk, Szymon Żerko, Michał Górka, Wiktor Koźmiński, Benjamin Bardiaux, Barbara Zambelli, Francesco Musiani, Mario Piccioli, Priyanka Basak, Faith C. Blum, Ryan C. Johnson, Heidi Hu, D. Scott Merrell, Michael Maroney, Stefano Ciuri

Helicobacter pylori HypA (HpHypA) is a metallochaperone necessary for maturation of [Ni,Fe]-hydrogenase and urease, the enzymes required for colonization and survival of H. pylori in the gastric mucosa. HpHypA contains a structural Zn(II) site and a unique Ni(II) binding site at the N-terminus. X-ray absorption spectra suggested that the Zn(II) coordination depends on pH and on the presence of Ni(II). This study was performed to investigate the structural properties of HpHypA as a function of pH and Ni(II) binding, using NMR spectroscopy combined with DFT and molecular dynamics calculations. The solution structure of apo,Zn-HpHypA, containing Zn(II) but devoid of Ni(II), was determined using 2D, 3D and 4D NMR spectroscopy. The structure suggests that a Ni-binding and a Zn-binding domain, joined through a short linker, could undergo mutual reorientation. This flexibility has no physiological effect on acid viability or urease maturation in H. pylori. Atomistic molecular dynamics simulations suggest that Ni(II) binding is important for the conformational stability of the N-terminal helix. NMR chemical shift perturbation analysis indicates that no structural changes occur in the Zn-binding domain upon addition of Ni(II) in the pH 6.3–7.2 range. The structure of the Ni(II) binding site was probed using 1H NMR spectroscopy experiments tailored to reveal hyperfine-shifted signals around the paramagnetic metal ion. On this basis, two possible models were derived using quantum-mechanical DFT calculations. The results provide a comprehensive picture of the Ni(II) mode to HpHypA, important to rationalize, at the molecular level, the functional interactions of this chaperone with its protein partners.
New Article in Journal of Biomolecular NMR
Jerzy Sitkowski, Wojciech Bocian, Elżbieta Bednarek, Mateusz Urbańczyk, Wiktor Koźmiński, Piotr Borowicz, Grażyna Płucienniczak, Natalia Łukasiewicz, Iwona Sokołowska, Lech Kozerski
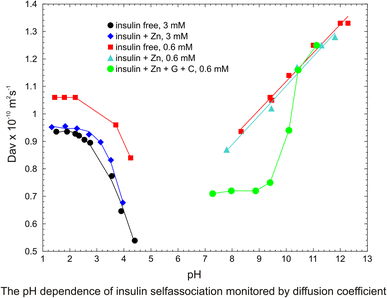
The NMR derived translational diffusion coefficients were performed on unlabeled and uniformly labeled 13C,15N human insulin in water, both in neat, with zinc ions only, and in pharmaceutical formulation, containing only m-cresol as phenolic ligand, glycerol and zinc ions. The results show the dominant role of the pH parameter and the concentration on aggregation. The diffusion coefficient Dav was used for monitoring the overall average state of oligomeric ensemble in solution. The analysis of the experimental data of diffusion measurements, using the direct exponential curve resolution algorithm (DECRA) allows suggesting the two main components of the oligomeric ensemble. The 3D HSQC-iDOSY, (diffusion ordered HSQC) experiments performed on 13C, 15N-fully labeled insulin at the two pH values, 4 and 7.5, allow for the first time a more detailed experimental observation of individual components in the ensemble. The discussion involves earlier static and dynamic laser light scattering experiments and recent NMR derived translational diffusion results. The results bring new informations concerning the preparation of pharmaceutical formulation and in particular a role of Zn2+ ions. They also will enable better understanding and unifying the results of studies on insulin misfolding effects performed in solution by diverse physicochemical methods at different pH and concentration.
|



















